Online Billing Portal Questions
How to View and Pay Your Bill Online
- Click the “Pay My Bill” button at the top of our web page
- If you have not registered yet, click the “Register for the first time” link. Otherwise continue logging in with the email and password you used when registering and continue to step 4.
- To register for the first time fill in all the required information on the form. A confirmation email will be sent that you will need to acknowledge in order to verify your email address. Please check your spam folders if this email is not received within a short period of time.
- Once logged in you will be able to view your last bill amount using the “View Bill” button.
- From this same page you can use the “Make a Payment” button to pay your current bill using either a credit card or via e-check.
- If you have any difficutlies accessing your account or making a payment feel free to call our local office at 607-589-6235.
How to Set Up Automatic Payments
- Log into the online billing portal at https://mybroadbandaccount.com/Haefele/
- Click the “Manage Payment Methods” under My Account
- If you have not added one already click the button to add a new Credit Card or Bank Account.
- Fill in all of the information for your Credit Card or Bank Account and make sure to check the “Use for Auto Payments” check box.
- Click the “Save Account” button.
- If you already have a Credit Card or Bank Account added then click the “Activate Auto Payment” button and select the account you would like to pay from.
How to Set Up Email Billing
- Follow the View and Pay your bill online steps above to access the Haefele Connect Account Portal.
- Once logged into your Account Portal, select the Setup Email Billing button from the My Account options on the left.
- You should see the email you used to log in under the list of emails. Using the red action button next to that email and select to make that the primary billing account.
- Alternativily you could add a new email address if you wish your bill to go to a different email than you used to set up your account portal.
- If you have any difficutlies setting up email billing please feel free to call our local office at 607-589-6235 for additional assistance.
General Internet Topics
Understanding Internet Bandwidth
Imagine the internet as a highway and internet bandwidth as the number of lanes on that highway. The more lanes there are, the more data can flow simultaneously, leading to a faster and smoother experience.
Here’s a breakdown of internet bandwidth:
What is it?
Internet bandwidth is the maximum amount of data that can be transferred over an internet connection in a given amount of time. It’s measured in bits per second (bps), with common units including:
- Megabits per second (Mbps): Commonly used for home internet connections.
- Gigabits per second (Gbps): For faster connections, especially for businesses or heavy data users.
Think of it like this:
- Downloading a large file: With a high bandwidth connection, the file will download quickly, like driving on a wide-open highway with no traffic.
- Streaming a video: A high bandwidth is crucial for seamless streaming, preventing buffering and interruptions.
- Multiple users online: If multiple devices are connected to the internet simultaneously, a higher bandwidth ensures everyone can enjoy smooth performance.
How is it measured?
Internet speed is often advertised as “download speed” and “upload speed.“
- Download speed: Refers to how fast you can receive data, such as when downloading a file or streaming a video.
- Upload speed: Refers to how fast you can send data, such as when uploading photos or videos to social media.
Both download and upload speeds are measured in Mbps or Gbps.
Factors affecting bandwidth:
- Internet plan: Your chosen internet plan determines the maximum bandwidth you can access.
- Wi-Fi connection: A weak Wi-Fi signal can decrease your bandwidth, even if you have a high-speed internet plan.
- Number of connected devices: The more devices connected to your network, the more bandwidth is shared, potentially impacting performance.
Here are some resources for further information:
- How Much Bandwidth Do You Need? (https://broadbandnow.com/bandwidth-calculator)
- Internet Speed Test (https://www.htva.net/manage-your-account/speed-test/)
By understanding internet bandwidth, you can choose the right internet plan for your needs and optimize your online experience. Don’t hesitate to contact us if you have any questions about your bandwidth or internet plan.
Factors Affecting Wi-Fi Speeds:
- Internet plan speed: Your chosen internet plan determines the maximum speed you can access, which often includes both wired and wireless speeds.
- Router capabilities: Your router’s technology and age can impact the speed and range of your Wi-Fi signal.
- Number of connected devices: The more devices connected, the more bandwidth is shared, potentially slowing down speeds.
- Distance from the router: The farther you are from the router, the weaker the Wi-Fi signal and the slower the speeds.
- Physical barriers: Walls, floors, and furniture can weaken the Wi-Fi signal and reduce speeds.
Tips for Optimizing Home Wi-Fi Speed
Want to enjoy smooth streaming, fast downloads, and uninterrupted online gaming? Here are some tips for optimizing your home Wi-Fi speeds:
Upgrade your router:
Newer routers offer faster speeds, better range, and support for newer technologies like Wi-Fi 6 and 6E. If you’re using an old router, consider upgrading to take advantage of these benefits. Confused by all the options? Let Haefele Connect managed the Wi-Fi for you with our Managed Wi-Fi Service.
Choose the right location for your router:
Place your router in a central location in your home away from walls, floors, and metal objects that can block the signal. Consider elevating the router for better signal propagation.
Use the 5 GHz band:
Most routers offer both 2.4 GHz and 5 GHz Wi-Fi bands. The 2.4 GHz band has a longer range but slower speeds, while the 5 GHz band offers faster speeds but shorter range. If you’re close to your router, use the 5 GHz band for the best performance. Many new routers will combine the 2.4 and 5 GHz bands and move devices between the two as needed. This gives you the best Wi-Fi possible based on distance and signal strength.
Limit the number of connected devices:
The more devices that are connected to your Wi-Fi network, the slower the speeds will be for everyone. Disconnect unused devices and consider using wired connections for devices like game consoles and streaming boxes.
Update your firmware:
Router manufacturers regularly release firmware updates that improve performance and fix bugs. Check your router’s manufacturer website for the latest firmware update and install it.
Upgrade to a Mesh Wi-Fi system
If you have a large home or areas with weak Wi-Fi signal, consider using a Mesh Wi-Fi system to improve coverage. All the mesh units worth together to blanket your home with Wi-Fi. Haefele Connect does not recommend induvidaul Wi-Fi extenders. We have found these cause more problems than they fix.
Reduce interference:
Other devices, such as cordless phones, microwave ovens, and Bluetooth speakers, can interfere with your Wi-Fi signal. Turn off or move these devices away from your router.
Use a wired connection when possible:
For devices that you use frequently, such as your computer or gaming console, use a wired Ethernet connection for the most stable and fastest performance.
Turn off Wi-Fi on unused devices:
Even when devices are not actively using Wi-Fi, they can still scan for networks and consume bandwidth. Turn off Wi-Fi on devices you’re not using to free up resources for other devices.
Use a guest network:
If you have a lot of guests who use your Wi-Fi, consider setting up a guest network. This will help to protect your home network from unauthorized access and prevent them from accessing your shared files or devices.
Monitor your network:
Many new routers include an app you can use to monitor your network. You should be able to use this app to ensure connected devices have good signal strength. If you have managed Wi-Fi from Haefele Connect you can use our CommandIQ app to monitor and control your network.
Wi-Fi Speeds by Router Generation
While the theoretical maximum speeds and the speeds listed by the router manufacturers for different Wi-Fi generations are impressive, the actual speeds you’ll experience will be lower for various reasons. Here’s a breakdown of what you can expect:
| Wi-Fi Generation | Theoretical Max Speed | Typical Real-world Speeds |
| 802.11a | 54 Mbps | 5-15 Mbps |
| 802.11b | 11 Mbps | 1-3 Mbps |
| 802.11g | 54 Mbps | 10-25 Mbps |
| 802.11n (Wi-Fi 4) | 600 Mbps | 50-150 Mbps |
| 802.11ac (Wi-Fi 5) | 6.8 Gbps | 100-300 Mbps |
| 802.11ax (Wi-Fi 6) | 9.6 Gbps | 200-800 Mbps |
Cable Modem Troubleshooting
Understanding the ports on your Modem
There are many different models of cable modems. The picture below is an example of just one of the many models that will work on Haefele Connect.
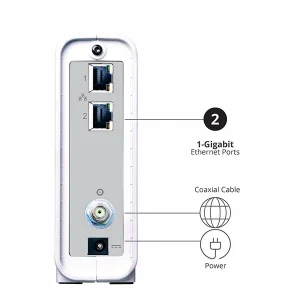
Power: 12v power from the supplied power pack
Coaxial Cable: Cable line input to your cable modem. This wire is specifically set up durring your install and the cable modem should not be moved to a different jack in your home. This connector should be slightly past finger tight.
Phone: POTS voice port to home phone if your cable modem is equipt
Ethernet: 1Gbps ethernet ports. Usually one will feed to your router and if there is more than one port on a non Wi-Fi cable modem only the top port should be used. The others will not be active.
Understanding the lights on your Modem
There are many different models of cable modems. The picture below is an example of just one of the many models that will work on Haefele Connect.

Power: Should be solid Blue or Green Depending on model. If power light is not on please confirm that the modem is plugged into a working outlet.
Downstream Light(Solid): Cable modem has locked on to the downstream signal and is working normaly. Light can be blue or green.
Downstream Light(blinking): Cable modem is attempting to aquire the downstream signal. If this continues for more than two minutes without going solid, there may be a signal issue. Check that COAX cable is screwed on tightly.
Upstream Light(Solid): Cable modem has locked on to the upstream signal and is working normaly. Light can be blue or green.
Upstream Light (blinking): Cable modem is attempting to aquire the upstream signal. If this continues for more than two minutes without going solid, there may be a signal issue. Check that COAX cable is screwed on tightly.
Internet Light (Solid): Internet is operational.
Internet Light (Blinking or Off): No Connection, verify all cable connections and try resetting the modem.
Troubleshooting a Cable Modem
There are many things that can lead to an offline or intermittent internet connect.
Check the physical connection:
- Verify that the power cord is plugged into a working outlet.
- Verify that the COAX cable is fully screwed into the cable modem. Connection should be just past finger tight.
- Verify that the ethernet cable is all the way plugged into the modems ethernet port and is plugged into either a router or directly into a single computer.
Are any devices able to access the internet?
- If any devices are able to access the internet then the cable modem is most likely working as it should.
- The issue could be with an induvidual device or with the router.
- It is recommended to power cycle both the cable modem and the router by removing power for at least 30 seconds. Cable modem should be powered back on fully first and then the router should be plugged back in.
Rebooting the Cable Modem
- A recommended first step to any internet issue is to fully reboot both the cable modem and the router.
- Power should be removed for at least 30 seconds from both the cable modem and the router if they are separate devices. The cable modem should be powered back on fully first and then the router should be plugged back in.
- If you are still unable to access the internet please reach out to our 24/7 technical support number.
Digital Phone Troubleshooting
Troubleshooting Phone Issues
No dial tone or “No Line” Message:
The most common cause of this issue is that a cord is either badly damaged or disconnected.
Check to make sure all phone cords are plugged in and securely in place.
Check the cords for damage as well. It is common for household pets or mice to chew on the wires and cause them to not function properly.
If your phone base unit is not plugged directly into the modem, and instead goes through a wall outlet, damage to the phone lines inside the wall may be the issue. Try plugging the phone base unit directly into the modem. If this resolves the issue, an electrician would need to be called to repair the lines inside the wall.
Call Audio Issues
The most common cause for call audio issues is either a damaged phone cord, or a loose connection.
Check to make sure there is no damage to the phone cords (folds, pinches, tears, or chews).
Check the connectors to make sure they are plugged in, and that the clip to secure them in place is working properly.
Calls cannot be completed or drop
Check the phone cord connections as above to make sure there is no loose connection or damage
If cords are secure and not damaged, please record the date/time of the phone calls, as well as the number the call was with. Report these examples to tech support so an investigation into the issue can begin.
Common Star Codes
Note: Some Feature Access Codes may not work on specific devices due to manufacturer specifications and configurations.
*62 Voice Portal
*86 Voicemail Retrieval
*72 Call Forwarding Activation
*73 Call Forwarding Deactivation
*69 Call Return
*78 Do Not Disturb Activation
*79 Do Not Disturb Deactivation
*66 Last Number Redial
Fiber ONT Troubleshooting
Understanding the ports on your ONT

Power: 12v power from the supplied power pack
Ethernet: 2.5 Gigabit Ethernet Port
Phone: POTS voice port to home phone
WAN: SC/APC Fiber Connection, fiber input from the outside of your house.
Understanding the Lights on your ONT

Power Light:
Green – ONT has power and everything is working as it should be
No Light – ONT is not receiving power, please check that the power supply is plugged into a working outlet.
Red – ONT failed to boot. Please unplug the power cord for 30 seconds and then plug it back in. Wait 2 minutes for ONT to fully boot and if light does not turn green after that amount of time please call tech support.
Broadband Light:
Green – ONT is communicating with Haefele Connect and everything is working properly.
Red – ONT is not receiving proper light levels. Please check that the fiber cable is plugged in the back of the unit and is not pinched or bent. Any bend tighter than the size of a quarter can cause light levels to drop. If light is still red please call tech support.
Service Light:
Green – ONT has been provisioned for the internet package you subsribe to.
Red – If the Power and Broadband light are both green but the Service Light is red please call tech support.
Ethernet Light:
Green – The ethernet light should blink green with activity.
No Light – Please ensure that the ethernet cable is plugged between the Ethernet port on the ONT and the WAN port on your router, and that your router is powered on.
Phone Light (for Digital Phone customers):
Green – Phone light will be solid green when you are on a phone call.
No Light – Normal for when your phone is on the hook.
Managed Wi-Fi Troubleshooting
Understanding the Light on Your Gigaspire Router
Depending on the model of Gigaspire Router there will either be a light bar on the upper corner of your router or a single light on the back as seen in the images below.


No Light: Unit does not have power. Check that the power cable is plugged in and that the power pack is plugged into a working outlet.
Amber Light (Slow Blink): Gigaspire is booting or upgrading firmware
Green Light (Steady): Gigaspire working normally and connected to the internet.
Red Light: Gigaspire has failed to boot or there is a service failure and no internet connection. Check that the ethernet cable is plugged in from the Modem/ONT and that the Modem/ONT is online and working.
Green Light (Blinking): WPS Enabled and attempting to connect to a device.
Understanding the Ports on Your Gigaspire Router
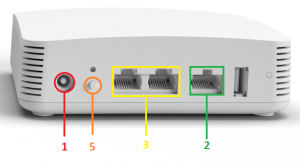
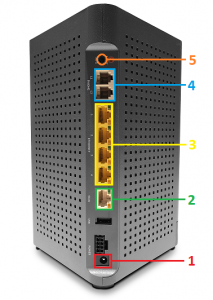
- 12v power input
- WAN port: ethernet connection to ONT/Router
- LAN Ports: ethernet connection to devices (computers)
- Telephone Ports: Not Used
- WPS button
How to Use the CommandIQ App
Here are some helpful videos on how to use the CommandIQ app. Click here for more information on CommandIQ.