Phishing is the most common tactic employed by hackers, as it requires the least amount of effort and generally preys on the less cyber-aware. It’s also the most common way for you to be exposed to ransomware. Phishing attacks can take many forms, but they all share a common goal – getting you to share sensitive information such as login credentials, credit card information, or bank account details.
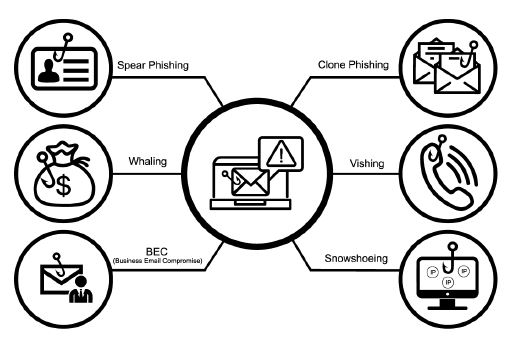
Here are some different types of phishing attacks to watch out for:
- Phishing: In this type of attack, hackers impersonate a real company that you know to obtain your login credentials. You may receive an e-mail asking you to verify your account details with a link that takes you to an imposter login screen that delivers your information directly to the attackers.
- Spear Phishing: Spear phishing is a more sophisticated phishing attack that includes customized information that makes the attacker seem like a legitimate source. They may use your name and phone number and refer to known companies in the e-mail to trick you into thinking they have a connection to you, making you more likely to click a link or attachment that they provide.
- Shared Document Phishing: You may receive an e-mail that appears to come from file-sharing sites like Dropbox or Google Drive alerting you that a document has been shared with you. The link provided in these e-mails will take you to a fake login page that mimics the real login page and will steal your account credentials.
To avoid these phishing schemes, please observe the following email best practices:
- Do not click on links or attachments from senders that you do not recognize. Be especially wary of .zip or other compressed or executable file types.
- Do not provide sensitive personal information, like usernames and passwords, over email.
- Watch for email senders that use suspicious or misleading domain names.
- Inspect URLs carefully to make sure they’re legitimate and not imposter sites.
- Do not try to open any shared document that you’re not expecting to receive.
- Be especially cautious when opening attachments or clicking links if you receive an email containing a warning banner indicating that it originated from an external source.

